
Tightening fasteners correctly is key in mechanical work. Most folks are familiar with torque specifications as the most common form of estimating fastener tension by how much force it takes to rotate the component. The fastener tension can vary at an identical torque spec under different conditions, and it is the tension that matters.

The friction against a fastener’s threads and/or flanges is a big factor in how much axial tension applied with a torque value. A bolt that has its threads and flange lubricated with oil has less friction as it is tightened compared to a dry bolt. This means that an oil lubricated bolt can apply more axial tension at the same torque value as a dry bolt. In the opposite direction, a dirty bolt with contaminated (or damaged) threads will have more friction than a clean dry bolt. The dirty bolt will have less axial tension than the clean dry bolt at the same torque value. This is why general torque specification are given for clean threads without lubrication.
The five valve cylinder heads of the 400 ~ 450 cc Yamaha high performance engines require their main cylinder head bolts and washers be cleaned and lubricated with molybdenum grease prior to installation. The bolts should be tightened evenly in a crisscross pattern to an initial specification. The bolts should be loosened evenly and removed. The excess moly grease should be cleaned away, and fresh moly grease applied to the bolt threads, flanges, and washers. The bolts are then reinstalled and tightened evenly to a second torque specification. Finally all of the bolts are tighten an additional 90 degrees in a crisscross pattern and then 90 degrees again to reach a position 180 degrees from their setting after the secondary torque.
An angle torque wrench can be used for accurate angle torquing.


If unavailable, mark the bolt and cylinder head (or other component) to note the change in position.



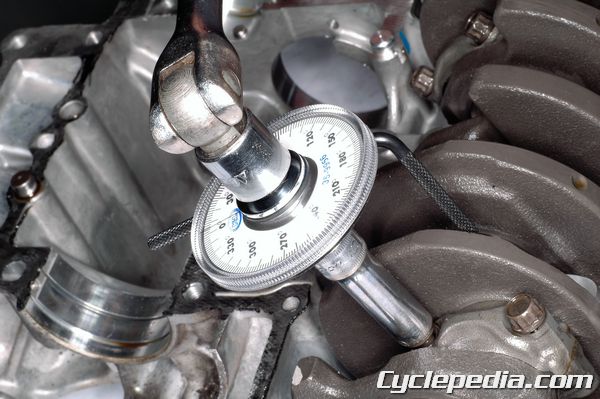
The 650 cc parallel twin engines found in Kawasaki’s Ninja, Versys, and Vulcan models have very specific instructions for tightening their connecting rod nuts and bolts. The bolts are designed to stretch when tightened and shouldn’t be reused once removed. The new nuts and bolts should be cleaned, dried, and lubricated with moly oil prior to use. Kawasaki provides two different methods of tightening theses fasteners. The recommended method is to measure the bolt length before and after installation in order to determine if the tension is correct based on bolt stretch. A fallback method is to tighten the nuts to a specified torque value and then an additional 120 degrees of rotation. In both cases Kawasaki stipulates exact specifications for using new or used connecting rods and nuts to make sure these critical fasteners have the correct tension, not just tightened to a torque value.

Some fasteners cannot be tightened with a standard socket or torque wrench. If an adapter like a crows foot, or locknut wrench is installed and changes the length of the torque wrench lever this must be taken into consideration with the formula W = (S x L) / E; where S = specified toque, W = adapted torque wrench value, L = torque wrench lever length, and E = total extended length of the torque wrench lever with adapter. Note, an adapter that is set at a right angle to the lever end doesn’t apply, only an extension that changes the lever length. For example if the specified torque (S) is 50 N-m, the lever length (L) is 300 mm and the extended lever length (E) is 375 mm the adapted torque wrench value (W) should be 40 N-m. If the service manual indicated the use of a special adapter in may also have an adapted torque wrench value for that special adapter.
Many crucial components use fasteners that require lubrication, specific tightening sequences, or one time use fasteners. Special requirement fasteners are often found with the cylinder head, connecting rods, main bearings, cam holders, suspension pivots, and brake caliper mounting bolts. It is important to follow the instructions in the service manual for tightening procedures to achieve the desired fastener tension. One should be familiar with the torque wrench function and understand how the torque value relates to fastener tension.

